Challenges Faced by Female Scientists: This study highlights significant challenges faced by female scientists in STEM disciplines, emphasizing ongoing gender inequality in academia. Despite female scholars’ high scientific activeness, particularly in publishing SDG5-related studies, their contributions are less recognized, as evidenced by significantly lower citation rates compared to their male counterparts. This disparity points to potential biases in academic evaluation processes, where female-led research receives 9% fewer citations per month on average than male-led work. These findings underscore the need for more inclusive and fair academic practices to ensure gender equality in scientific recognition and impact.
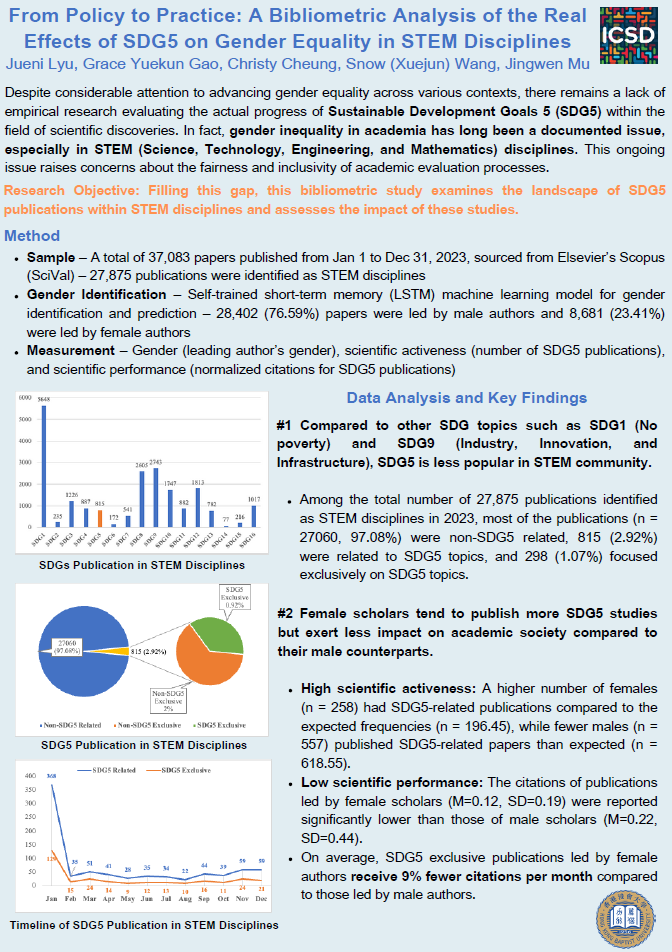
Enormous Dataset: The study utilized a substantial dataset, analyzing 37,083 papers published in 2023, with a focus on 27,875 publications within STEM disciplines. By employing a self-trained LSTM machine learning model for gender identification, the research processed an impressive volume of data, identifying 28,402 papers led by male authors and 8,681 by female authors. Additionally, it examined 815 SDG5-related papers, including 298 exclusively focused on SDG5, allowing for a detailed and comprehensive analysis of gender disparities in scientific impact and recognition. This extensive dataset provided a robust foundation for uncovering the challenges faced by female scientists in academia.
More on: ICSD 2024: Paper & Poster Presentations Agenda (with session links) – Airtable

